8.4. Standard Time and Time Zones
If each town were to keep the time of its own meridian, there would be much difference in local time between one town and the other. 10 a.m. in Georgetown, Penang would be 10.10 in Kota- Bharu (a difference of 2½° in longitude). In larger countries such as Canada U.S.A., China, India, and Russia the confusion arising from the differences alone would drive the people mad. Travellers going from one end of the country to the other would have to keep their appointments. This is impracticable and very inconvenient.
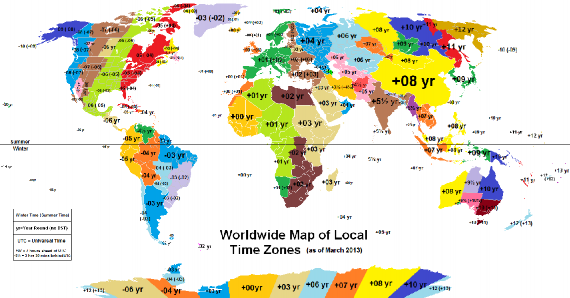
To avoid all these difficulties, a system of standard time is observed by all countries. Most countries adopt their standard time from the central meridian of their countries. The Indian Government has accepted the meridian of 82.5° east for the standard time which is 5hrs. 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. The whole world has in fact been divided into 24 Standard Time Zones, each of which differs from the next by 15° in longitude or one hour in Time. Most countries adhere to this division but due to the peculiar shapes and locations of some countries, reasonable deviations from the Standard Time Zones cannot be avoided.
Larger countries like U.S.A. (9), Canada (6) and Russia (9) which have a great east-west stretch have adopted 9, 6 and 9 time zones respectively for practical purposes.
Daylight saving time (DST) is a change in the standard time with the purpose of getting better use of the daylight. Typically, clocks are adjusted forward one hour near the start of spring and are adjusted backward in the autumn. Although it has only been used in the past hundred years, the idea of DST was first conceived many years before.
