Figure 1: Classification of Resources
3. Energy Resources
Energy is an essential input for economic development and improving the quality of life. It is required for generation of power, required by agriculture, industry, transport and other sectors of the economy. Energy may be classified into two categories, namely:
♤ Conventional – Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas and electricity
♤ Non-conventional – solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, and biogas energy Other classification can be made between –
♤ Non-renewable resources – which when exhausted are exhausted forever such as coal etc.
♤ Renewable resources – which are inexhaustible such as wind energy, solar energy etc.
3.1. Coal
Coal is a one of the important minerals which is mainly used in the generation of thermal power and smelting of iron ore. It is the one of the most mined mineral from the earth. According to one estimate, proven coal reserves are 860, 938 million tonnes.
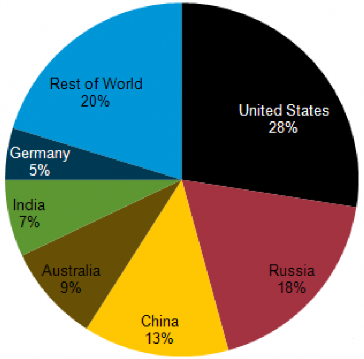
Of the three fossil fuels (Petroleum, natural gas and coal), coal has the most widely distributed reserves; coal is mined in over 100 countries, and on all continents except Antarctica. The largest proved reserves are found in the United States, Russia, China, Australia and India (figure 2). A proved recoverable reserve is the tonnage of coal that has been proved by drilling etc. and is economically and technically extractable. Coal is found majorly in forms of Lignite [1] and Anthracite. Distribution of coal across the world is shown in figure 3.