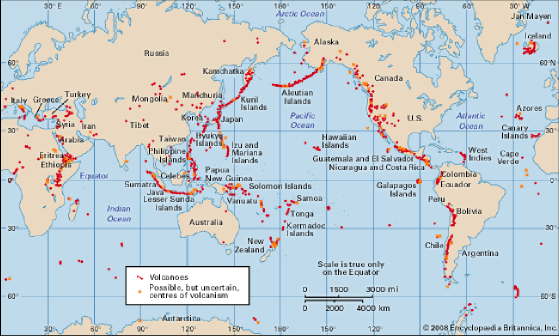
3.5. Distribution of Volcanoes
The volcanoes are mostly associated with the weaker zones of the Earth's crust which are also zones of seismic activities like the earthquakes. The weaker zones are mostly found in the areas of fold mountains. They are also associated with the meeting zones of oceans and continents, or with the mountain building activity.
Most of the world's active volcanoes are associated with the plate boundaries. About 15 per cent of the volcanoes are associated with the divergent plate boundaries and about 80 per cent with the convergent plate boundaries. Some volcanoes are also found in the intra-plate regions.
The main volcanic belts are as under:
1. Circum-Pacific Belt: It includes the volcanoes of the eastern and western coastal areas of the Pacific Ocean. This belt is also known as the Ring of Fire of the Pacific Ocean.
It begins from Erebus mountains of Antarctica and runs northwards through Andes of South America and Rockies of North America to reach Alaska. From there, it turns eastwards along the coast of Asia to include the volcanoes of Sakhalin and Kamchatka, Japan and Philippines respectively. This belt finally merges with the Mid-continental Belt in Indonesia.
Most of the high volcanic cones and volcanic mountains are found in the Circum-Pacific Belt. Cotopaxi in Andes (5896 m) is the highest volcanic mountain in the world. The other famous volcanoes are Fujiyama (Japan), Shasta, Rainier, Mt St Helena (USA).
2. Mid-Continental Belt: It includes the volcanoes of the Alpine mountains and the Mediterranean Sea. The volcanic eruptions are caused due to the convergence and collision of the Eurasian Plates and the African and Indian Plates. Some of the famous volcanoes of the Mediterranean Sea such as the Stromboli, Vesuvius, Etna, etc., are in this belt. This belt is not continuous and has several volcanic free zones such as the Alps and the Himalayas. The important volcanoes in the fault zone of eastern Africa are Kilimanjaro, Meru, Elgon, Rungwe, etc.
3. Mid-Atlantic Belt: It includes the volcanoes along the mid-Atlantic ridge which is the divergent plate zone. They are mainly of the fissure eruption type. Iceland, is the most active volcanic area.