Figure 2: Distribution of Earthquake belts
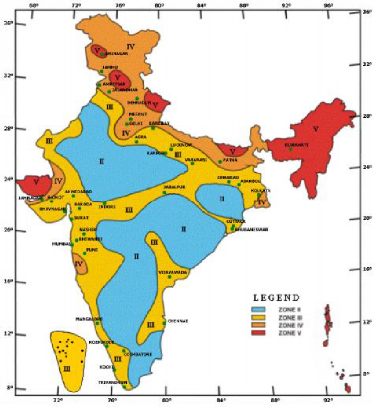
1.5.2. Seismic Zones of India
The Indian sub-continent is highly prone to multiple natural disasters including earthquakes, which is one of the most destructive natural hazards with the potentiality of inflicting huge loss to lives and property. Earthquakes pose a real threat to India with 59% of its geographical area vulnerable to seismic disturbance of varying intensities including the capital city of the country.
The varying geology at different locations in the country implies that the likelihood of damaging earthquakes taking place at different locations is different. Thus, a seismic zone map is required so that buildings and other structures located in different regions can be designed to withstand different level of ground shaking. The current zone map divides India into four zones – II, III, IV and V.