Problem of Waste Deposits in Space
Space debris, also known as orbital debris, space junk, and space waste, is the collection of defunct objects in orbit around Earth. This includes everything from spent rocket stages, old satellites, fragments from disintegration, erosion, and collisions. Since orbits overlap with new spacecraft, debris may collide with operational spacecraft.
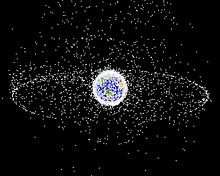
Space debris populations seen from outside geosynchronous orbit (GEO). Note the two primary debris fields, the ring of objects in GEO, and the cloud of objects in low earth orbit (LEO).
As the chance of collision is influenced by the number of objects in space, there is a critical density where the creation of new debris is theorized to occur faster than the various natural forces remove them. Beyond this point, a runaway chain reaction may occur that would rapidly increase the number of debris objects in orbit, and therefore greatly increase the risk to operational satellites. Called the "Kessler syndrome", there is debate if the critical density has already been reached in certain orbital bands. A runaway Kessler syndrome would render a
portion of the useful polar-orbiting bands difficult to use, and greatly increase cost of space launches and missions. Measurement, growth mitigation and active removal of space debris are activities within the space industry today.

India has done studies related to waste deposits in space referred as Space Debris and successfully developed methodologies and software tools. ISRO performs Space Object Proximity Analysis for its operational Low Orbit spacecrafts on a regular basis to assess the collision risk and determine risk mitigation strategies in advance. Collision Avoidance analysis is also carried out to identify the safe lift-off time for launching of satellites from Sriharikota. The growing space debris poses threat to present and future space activities, globally, in terms of collision risk. ISRO has taken mitigation measures like passivation of spent upper stage of launch vehicles and de- orbiting of non-functional satellites to avoid creation of space debris. ISRO has also undertaken collaborative studies with other space agencies to control and restrict this outer space contamination. India is a active member of Inter Agency Space Debris Co-ordination Committee (IADC) and played a key role in evolving space debris mitigation guidelines formulated by IADC and United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS).
