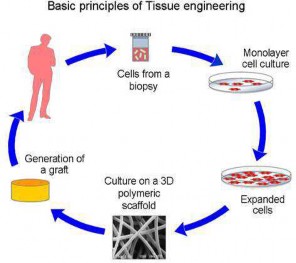
34.TISSUE ENGINEERING-
♤ Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physio-chemical factors to improve or replace biological functions.
♤ While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver).
♤ Tissue Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that applies the principles of Biology, Chemistry, Physics and Engineering for the development of substitutes that replace, repair or enhance biological function of diseased and damaged human body parts, by manipulating cells via their extracellular microenvironment. This three dimensional extracellular architecture ("scaffold") can be fabricated in the shape of the tissue we want to restore