86. NET METERING
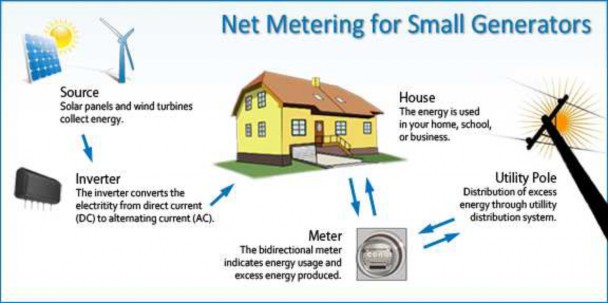
Net metering allows residential and commercial customers who generate their own electricity from solar/renewable power to feed electricity they do not use back into the grid. Delhi, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Bihar, Gujarat, West Bengal and Maharashtra have adopted net metering for renewable power
♤ Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid. For example, if a residential customer has a PV system on the home's rooftop, it may generate more electricity than the home uses during daylight hours. If the home is net-metered, the electricity meter will run backwards to provide a credit against what electricity is consumed at night or other periods where the home's electricity use exceeds the system's output. Customers are only billed for their "net" energy use. On average, only 20-40% of a solar energy system’s output ever goes into the grid. Exported solar electricity serves nearby customers’ loads.
♤ Without net metering, a second meter is usually installed to measure the electricity that flows back to the provider, with the provider purchasing the power at a rate much lower than the retail rate.