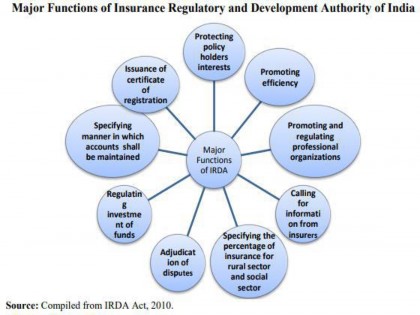
(a) Powers and functions
♤ Issuing a certificate of registration to the applicant and suspend/ cancel such registration;
♤ Protection of the interests of the policy holders in matters concerning assigning of policy, nomination by policy holders, insurable interest, settlement of insurance claim, surrender value of policy and other terms and conditions of contracts of insurance;
♤ Specifying requisite qualifications, code of conduct and practical training for intermediary or insurance intermediaries and agents;
♤ Promoting efficiency in the conduct of insurance business;
♤ Calling for information from, undertaking inspection of, conducting enquiries and investigations including audit of the insurers, intermediaries, insurance intermediaries and other organizations connected with the insurance business;
♤ Control and regulation of the rates, advantages, terms and conditions that may be offered by insurers in respect of general insurance business not so controlled and regulated by the Tariff Advisory Committee;
♤ Regulating investment of funds by insurance companies;
♤ Adjudication of disputes between insurers and intermediaries or insurance intermediaries.
Scheme of Insurance Ombudsman:
♤ With an objective of providing a forum for resolving disputes and complaints from the aggrieved insured public against Insurance Companies, the Government of India brought "Insurance Ombudsman Rules, 2017".
♤ These Rules aim at resolving complaints relating to the settlement of disputes with Insurance Companies and their agents and intermediaries in a cost effective, efficient and impartial manner.
♤ These Rules apply to all the Insurance Companies operating in General Insurance business and Life Insurance business, in Public and Private Sector.

To implement the above Rules, the Institution of Insurance Ombudsman has been established and is functioning since 1999. The Ombudsman functions within a set geographical jurisdiction and can entertain disputes relating to:
a) Delay in settlement of claims
b) Any partial or total repudiation of claims by an insurer.
c) Any dispute over premium paid or payable in terms of the policy
d) Misrepresentation of policy terms and conditions at any time in the policy document or policy contract
e) Any dispute on the legal construction of the policies in so far as such disputes relate to claims.
f) Policy servicing related grievances against insurers and their agents and intermediaries
g) Issuance of life insurance policy, general insurance policy including health insurance policy which is not in conformity with the proposal form submitted by the proposer.
h) Non-issue of any insurance policy to customers after receipt of premium in life insurance and general insurance including health insurance.
i) Any other matter resulting from the violation of provisions of the Insurance Act, 1938 or the regulations, circulars, guidelines or instructions issued by the IRDAI from time to time or the terms and conditions of the policy contract, in so far as they relate to issues mentioned at clauses(a) to (f).
The Insurance Ombudsman is provided with a Secretarial Staff by the IRDAI as may be determined by the Executive Council of Insurers. The total expenses on running the Institution are borne by the Life Insurance Council AND THE General Insurance Council in such proportion as the Executive Council of Insurers may, by a general or special order specify, from time to time.
