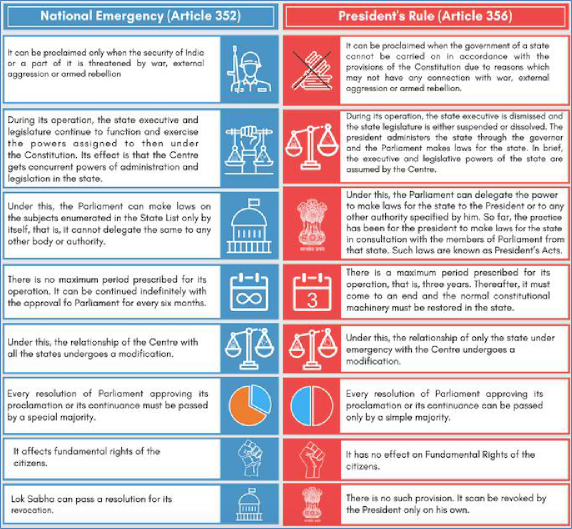
3.3. Difference between National Emergency & President rule:
3.4. Effects of State Emergency
The President acquires the following extraordinary powers when the President’s Rule is
imposed in a state:
1. He can take up the functions of the state government and powers vested in the governor or any other executive authority in the state.
2. He can declare that the powers of the state legislature are to be exercised by the Parliament.
3. He can take all other necessary steps including the suspension of the constitutional provisions relating to anybody or authority in the state.
♤ When the President’s Rule is imposed in a state, the President dismisses the State Council of Ministers, headed by the Chief Minister (however, the powers of the High Court are not affected). The State Governor, on behalf of the President, carries on the State administration with the help of the Chief Secretary of the State, or the advisors appointed by the President.
♤ State assembly may be dissolved or suspended depending upon prevailing circumstances.
o Such a Proclamation may declare that the powers of the State Legislature shall be exercisable by or under the authority of Parliament.
♤ As per Article 357, the Parliament may confer this legislative power on the President and authorize him to further delegate it to any other authority.
o The Parliament can authorize the President to sanction expenditure from the
