2. Alternative Dispute Redressal Mechanisms

Under constitution, ADR can find its basis in the
♤ Article 14 (Equality before Law)
♤ Article 21 (Right to life and personal liberty)
♤ Article 32 (Right to Constitutional remedies) which provides for the right of people to seek justice.
♤ Article 39A of DPSP which provides for Equal Justice and Free legal Aid.
ADR mechanism of settling any dispute includes Arbitration, Conciliation, Mediation, settlement through Lok Adalat and with the intervention of Family Court, Judicial Settlement, Plea Bargaining, and Collective Bargaining etc.
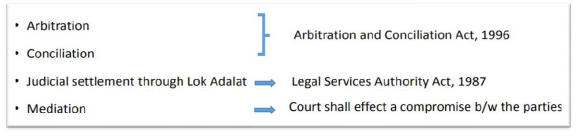
Further, Section 89 of the Civil Procedure Code provides for Settlement of disputes outside the court through the following methods:
The ADR processes conform only to civil disputes, as explicitly provided by law. ADR process may be binding or non-binding, voluntary or mandatory depending upon various circumstances and contractual relation between the parties. In India this mechanism is not new but what is new is its proliferation in the modern days.
In general, the entire globe of ADR can be divided under two major sub-heads: arbitration and mediation. Arbitration is consent based adjudication processes outside the traditional judicial system of the court by an independent person or institution, whereas mediation is a process of settlement between the parties with the help of independent person/intuition. In ADR active roles are envisaged to be played by the parties to dispute, lawyers representing them, the court/forum before which dispute is brought or pending and the person/ intuitions facilitating the settlement of dispute.
