Issues with Collegium System of Appointment
♤ View of Constituent Assembly: It had rejected the proposal to vest the Chief Justice with veto power over appointments.
♤ Violation of constitutional Provision: According to 214th Law commission of India Collegium is a clear violation of Article 74 of the Constitution of India which demand President to act on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers.
♤ Undemocratic: Collegium system is non-transparent and closed in nature as there exists no system of checks and balances which is essential to a democracy.
♤ Disturbing Balance of Power by the Second Judges case as provided by the constitution between executive and judiciary.
♤ Uncle Judges Syndrome: Law Commission in its 230th report said that nepotism, corruption and personal patronage is prevalent in the functioning of the collegium system
♤ Merit vs Seniority: There have been numerous cases where people with better qualifications and better track records have been sidelined to make way for someone incompetent due to seniority rule.
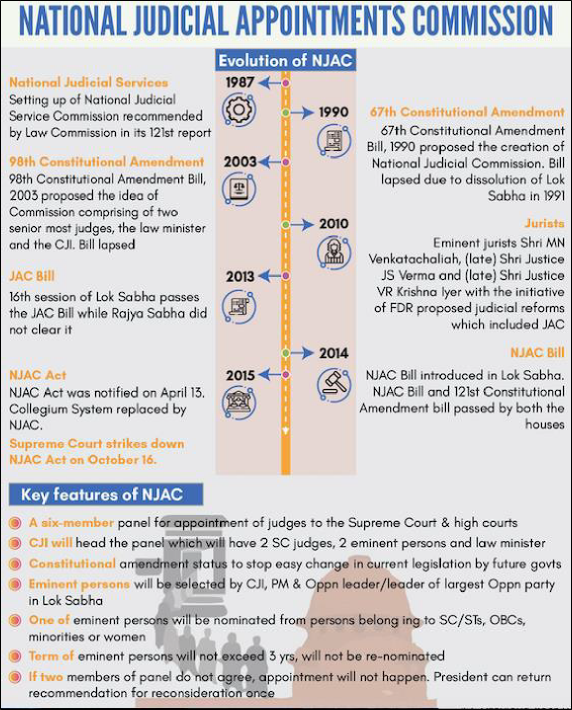
3.1.2.2. National Judicial Appointment Commission (NJAC)
♤ The government had established National Judicial Appointment Commission by way of 99th Constitutional Amendment.
♤ It was proposed constitutional body to replace the Collegium system of appointing judges.
o It was envisaged as an independent commission to appoint and transfer judges of High Court and appoint judges of Supreme Court of India.
o It was composed of three senior judges, two eminent outsiders and the Law Minister.
♤ However, before it was notified, it was challenged in Supreme Court as an attempt by government to interfere with the independence of the judiciary.

♤ To enable Separation of Powers between executive and judiciary as directed by Constitution of India.
independence of
the
violating
judiciary
Primacy of the judiciary is required as
♤ Government is major litigant: Since the government is a major litigant, giving it an edge in appointments would amount to fixing the courts.
♤ Independence of Judiciary: It has been regarded as basic structure of constitution and NJAC was termed as
