5.3. Principles of Social Audit
Eight specific key principles have been identified from Social Auditing practices around the world:
1. Multi-Perspective/Polyvocal: Reflect the views of all the stakeholders.
2. Comprehensive: Report on all aspects of the organisation's work and performance.
3. Participatory: Encourage participation of stakeholders and sharing of their values.
4. Multidirectional: Stakeholders share and give feedback on multiple aspects.
5. Regular: Produce social accounts on a regular basis so that the concept and the practice become embedded in the culture of the organisation covering all the activities.
6. Comparative: Provide a means whereby the organisation can compare its performance against benchmarks and other organisations’ performance.
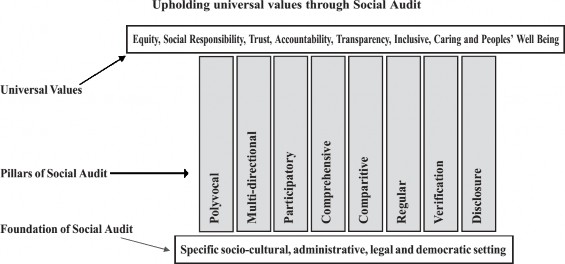

7. Verified: Social accounts are audited by a suitably experienced person or agency with no vested interest in the organisation.
8. Disclosed: Audited accounts are disclosed to stakeholders and the wider community in the interests of accountability and transparency.
These are the pillars of Social Audit, where socio-cultural, administrative, legal and democratic settings form the foundation for operationalising Social Audit.
