2.1. What are Civil Societies?
According to the World Bank, Civil Society refers to refers to a wide array of organizations, community groups, non-governmental organizations [NGOs], labour unions, indigenous groups, charitable organizations, faith-based organizations, professional associations and foundations.
♤ Globally, the term ‘Civil Society’ became popular in 1980s, when it started to be identified with non-state movements defying authoritarian regime, especially in Eastern Europe and Latin America.
♤ When mobilized, civil society - sometimes called the “third sector” (after government and commerce) - has the power to influence the actions of elected policy-makers and businesses.
♤ Examples of well-known civil society organizations include Amnesty International, the International Trade Union Confederation, World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), Greenpeace and the Danish Refugee Council (DRC).
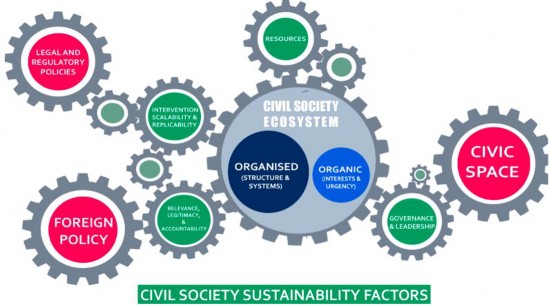
Following representation illustrate various factors that are important for survival and sustainability of civil society.