Fig. 5 Areas of Intensive Subsistence Agriculture
2.3.2. Plantation Agriculture
Plantation agriculture as mentioned above was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics. Some of the important plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane, bananas and pineapples. The characteristic features of this type of farming are large estates or plantations, large capital investment, managerial and technical support, scientific methods of cultivation, single crop specialisation, cheap labour, and a good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the export of the products.
The French established cocoa and coffee plantations in west Africa. The British set up large tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka, rubber plantations in Malaysia and sugarcane and banana plantations in West Indies. Spanish and Americans invested heavily in coconut and sugarcane plantations in the Philippines. The Dutch once had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia.
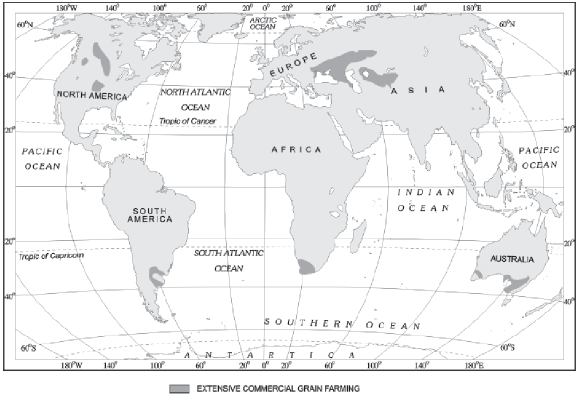
2.3.3. Extensive Commercial Grain Cultivation
Commercial grain cultivation is practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid- latitudes. Wheat is the principal crop, though other crops like corn, barley, oats and rye are also grown. This type of agriculture is best developed in Eurasian steppes, the Canadian and American Prairies, the Pampas of Argentina, the Velds of South Africa, the Australian Downs and the Canterbury Plains of New Zealand.