3.3. Natural Gas
Natural gas is a fossil fuel formed when layers of buried plants, gases, and animals are exposed to intense heat and pressure over thousands of years. The energy that the plants originally obtained from the sun is stored in the form of chemical bonds in natural gas. Natural gas, a nonrenewable energy resource, is found in deep underground rock formations or associated with other hydrocarbon reservoirs in coal beds and as methane clathrates. Petroleum is another resource and fossil fuel found in close proximity to, and with natural gas.
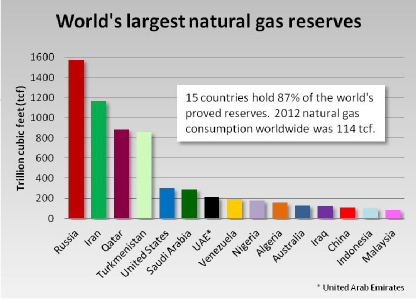
Like Petroleum, natural gas is not distributed evenly around the world. More than three-fourth
of the world’s proved natural gas reserves are located in top ten countries (figure 7). Following the Russia are Iran and Qatar, Turkmenistan, USA. Small gas fields are located in various parts of the world. [2]. Unconventional sources of natural gas are:
♤ Shale gas
♤ Coalbed methane (CBM)
♤ methane hydrates