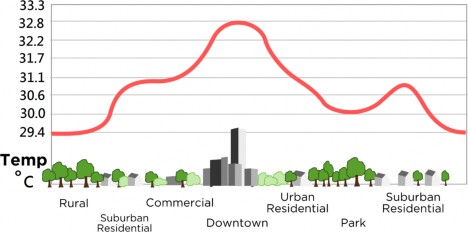
2.1. Urban Heat Island
The term "heat island" describes built up areas that are hotter than nearby surrounding areas. An urban heat island (UHI) is a metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The phenomenon was first investigated and described by Luke Howard in the 1810s. The temperature difference usually is larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds are weak. The typical temperature difference is several degrees between the center of the city and surrounding fields. It can be as high as 10 °C.

4 There is much greater variation in barometric pressure during the winter than during the summer. On average, high pressure systems are higher pressure and low pressure systems are lower pressure. This leads to a more rapid flow of air between the systems. This fluctuation is caused by much greater variation in temperature during the winter. While most summer days are roughly the same temperature, winter temperatures fluctuate dramatically.