Figure 3 – global precipitation pattern during El Nino

2 Thermocline – is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, such as an ocean or lake, or air, such as an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more rapidly with depth than it does in the layers above or below.
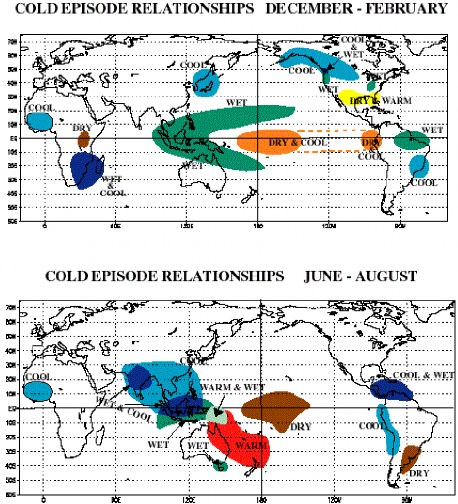
1.2. La Niña
La Niña (Spanish: meaning “The Girl Child”) is a counterpart of El Niño. During La Niña, the cold pool in the eastern tropical Pacific intensifies and the trade winds strengthen. During a period of La Niña, the sea surface temperature (SST) across the equatorial Eastern Central Pacific Ocean will be lower than normal by 3–5 °C.
Effects of LA NIÑA
♤ Africa - La Niña results in wetter-than-normal conditions in Southern Africa from December to February, and drier-than-normal conditions over equatorial East Africa over the same period.
♤ Asia - During La Niña years, the formation of tropical cyclones, along with the subtropical ridge position, shifts westward across the western Pacific ocean, which increases the landfall threat to China. Generally, South Asian monsoon is good during La Nina events as it strengthens the Indian Ocean loop of walker cell.