2.2.9. Earthquake Waves
Earthquakes1 are caused by the movements in the interior of the earth. These movements cause waves inside the earth just as waves are generated on the surface of water in a lake when a stone is thrown into it. Incidentally, majority of the earthquakes originate in the upper mantle.
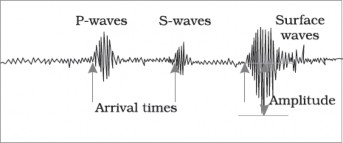
The earthquake waves are measured on the seismograph. The study of earthquake waves helps earth-scientists to get a lot of information about the types of rocks and layered composition in the interior of the earth.
Earthquake waves are basically of two types — body waves and surface waves. Body waves are generated due to the release of energy at the focus (origin of earthquake) and move in all directions travelling through the body of the earth. Hence, the name body waves. The body waves interact with the surface rocks and generate new set of waves called surface waves. These waves move along the surface. The velocity of waves changes as they travel through materials with different densities. The denser the material, the higher is the velocity. Their direction also changes as they reflect or refract when coming across materials with different densities.
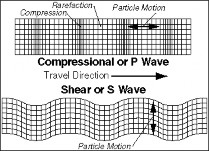
There are two types of body waves: P-waves and S-waves. Important surface waves are Rayleigh waves and L-waves (named after A. E. H. Love).
Body Waves | Surface Waves | |
‘P’- Waves’ or Primary waves | ‘S’- Waves’ or Secondary waves | L-waves |
I. These are ‘Longitudinal Waves’. II. Under their influence particles are displaced in backward-forward direction. (compression waves.) III. Their velocity is the fastest. IV. Their average velocity is 6-15 kilometers per second. V. Different densities of rocks have different velocities. VI. They can travel through all mediums – solids, liquids and gases. | I. These are transverse waves. II. Under their impact particles swing side by side (shear waves). III. Their velocity is lower than the primary waves. IV. These waves cannot pass through liquids. They travel through solids only. | I. These are transverse waves. II. Their propagation is limited to the surface of the earth only. III. Their velocity through solid particles or rocks is about 3.5 kilometers per second. IV. They cause the greatest damage and destruction of property during the earthquake. |