Table 3 – Different rainfall regions of India
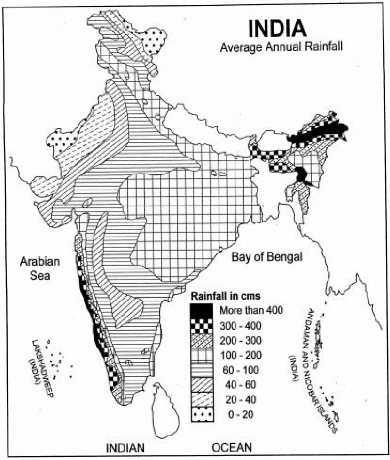
Figure 13 – India: Annual rainfall
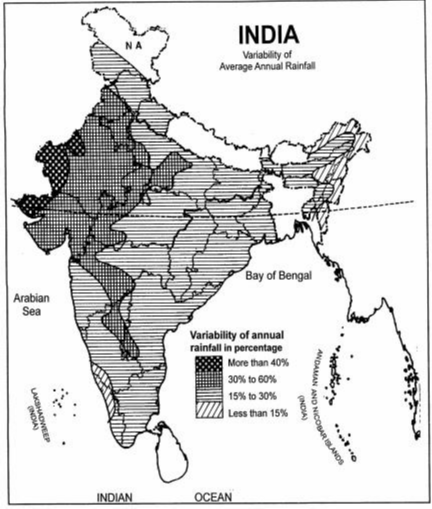
6. Variability of Annual Rainfall
Variability of rainfall refers to variations in rainfall from the average amount. The variability of rainfall is computed with the help of the following formula:
C.V. = (Standard Deviation / Mean) x 100; where C.V. is the coefficient of variation.
Study of variability of rainfall in an agricultural country such as India is very important. The rainfall in India is highly variable. The actual rainfall of a place in a year deviates from its average rainfall by 10 to over 60 per cent. The mean annual rainfall variability of rainfall in India has been plotted in figure 14. Description of annual rainfall’s variability is details as:
♤ It may be noted from figure 13 and figure 14 that the highest variability is found in the areas where the average annual rainfall is the lowest such as desert areas of Rajasthan. Here, variability of rainfall is around 60 per cent.
♤ Contrary to this, in the areas where the average annual rainfall is over 200 cm (Meghalaya plateau, Western Ghats), the annual variability of rainfall is less than 10 per cent.
♤ A very large part of India falls in the category of 15 to 30 per cent annual variability of rainfall. Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra etc. fall in this category
♤ Variability of annual rainfall increases from the western coast to the interior of the Peninsular region and from West Bengal and Odisha towards north and north-west.