Table 3 – difference between frontogenesis and frontolysis
As a result of the observations of atmospheric conditions at the surface and aloft, the following types of fronts are identified:
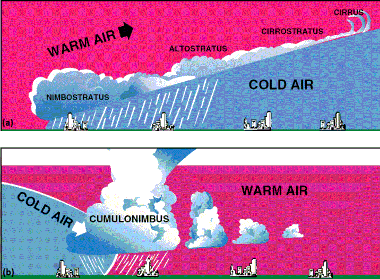
6.1. Warm Front
When a warmer and lighter air mass moves against an existing cold and dense airmass, it rises over the coldet and denser air mass. This type of front is known as warm front. (figure 26a). As the warm air gradually ascends the gently sloping surface of the wedge of cold air lying ahead, it cools. This cooling leads to the cloudy condensation and precipitation. Unlike the cold front, the changes in temperature and wind direction are gradual.