5. Air Mass
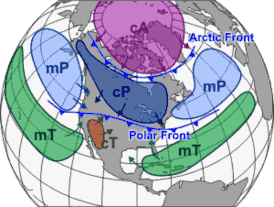
When the air remains over a homogenous area for a sufficiently longer time, it acquires the characteristics of the area. Such homogenous areas have uniform characteristics in terms of temperature, pressure and moisture. The air with distinctive characteristics in terms of temperature and humidity is called an air mass. It is defined as a large body of air having little horizontal variation in temperature and moisture. The homogenous surfaces, over which air masses form, are called the source regions. There are five major source regions. These are:
1. Warm tropical and subtropical oceans
2. The subtropical hot deserts
3. The relatively cold high latitude oceans
4. The very cold snow covered continents in high latitudes
5. Permanently ice covered continents in the Arctic and Antarctica
The air masses are classified according to the source regions. Air masses originated from tropical region are warm while those originated from polar region are cold. Air masses originated from these regions are called primary air masses. Accordingly, following types of airmasses are recognised: