7.4. Features of Overview
Youthful Stage – Upper course | Mature Stage – Middle Course | Old Stage –Lower Course | |
Characteristics | ♤ Vertical and headward erosion ♤ Rough channel bed ♤ High competence, low capacity ♤ Large gradient / slope ♤ High turbulence ♤ Narrow channel ♤ Straight course | ♤ Vertical and Lateral erosion ♤ Wider and deeper channel ♤ Competence decreases, capacity increases | ♤ Deposition ♤ Lateral erosion ♤ High discharge & velocity ♤ High capacity, low competence ♤ Meandering course ♤ Wide flood plain ♤ Channel depth & width at maximum ♤ Low gradient/slope |
Features | v-shaped valley, waterfalls, rapids, potholes, gorges, braided streams, Interlocking spurs | Meanders, river cliffs, slip off slopes, flood plains, | Levees, deltas, point bars, sand bars, oxbow lakes, meanders, larger flood plain, raised banks |
Coastal processes are the most dynamic and hence most destructive. The coastline of any place is always affected by the dynamic processes operating on the coasts, such as tides, waves and current.
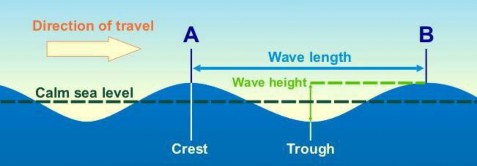
Tides and currents when come in contact with the shore have very little direct impact on the coastline. Instead, Waves are the prime agents of erosion in coastal regions. Waves are the result of transfer of energy from atmosphere to water by the wind moving over the water surface. The size of a wave is dependent upon wind velocity, wind duration and the area or distance over which the wind is traveling.