7.1.1. Erosion
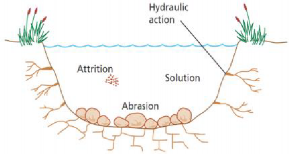
It is the removal of rock or soil. Stream erosion takes place through four processes – hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition and solution
♤ Solution or Corrosion- This is the chemical action of river water. The acids in the water slowly dissolve the bed and the banks. This occurs in streams running through rocks such as chalk and limestone.
♤ Abrasion or Corrasion- As the rock particles bounce, scrape and drag along the bottom and sides of the river, they break off additional rock fragments. This form of erosion is called corrasion. This is the mechanical grinding of the rivers against the banks and bed of the river. The erosional mechanism of abrasion operation in two ways
(i) Lateral Corrasion: This is sideways erosion which widens the river valley.
(ii) Vertical Corrasion: This is the downward erosion which deepens the river valley.
♤ Attrition- is the mechanical tear and wear of the erosional tools in themselves. The boulders, cobbles, pebbles etc. while moving with water collide against each other and thus are fragmented into smaller and finer pieces in the transit.
♤ Hydraulic Action- involves the breakdown of the rocks of valley sides due to the impact of water currents of channel. In fact, hydraulic action is the mechanical loosening and removal of materials of rock by water alone. No load or material is involved in this process.