1.1.1. Fold Mountains
These mountains are the most widespread and also the most important. They are caused by large-scale earth movements, when stresses are set up in the earth's crust. Such stresses may be due to:
♤ the increased load of the overlying rocks,
♤ flow movements in the mantle,
♤ magmatic intrusions into the crust, or
♤ the expansion or contraction of some part of the earth.
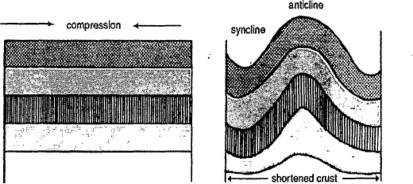
When such stresses are initiated, the rocks are subjected to compressive forces that produce wrinkling or folding along the lines of weakness. As illustrated in Fig.1 and 2, folding effectively shortens the earth's crust, creating from the original level surface a series of 'waves'.