Land not Suitable for Cultivation
Class V: Very well suited for grazing and forestry but not for cultivation of crops. It has a very good carrying capacity of livestock but needs protection from gullying.
Class VI: Well suited for grazing and forestry but not for cultivation of crops. It has a moderate carrying capacity of livestock. This land has steep slope, severe erosion, stoniness,, poor moisture retaining capacity, sainity and severe climate.
(iii) Multi-element (Statistical) Technique
(iv) Quantitative-cum-Qualitative Technique
(i) Empirical Technique: It is largely based on the experience of the fanners and the observed facts. Von Thunen was the 1st scholar who adopted the empirical technique and prepared the first agricultural land use and crop intensity models.
The empirical technique gives a generalised picture of the cropping pattern and agricultural regions. By adopting the empirical technique Symons, Munton and Morgan demarcated the agricultural regions of the different parts of the world. This technique, has, however, been criticised as it is not objective and scientific.
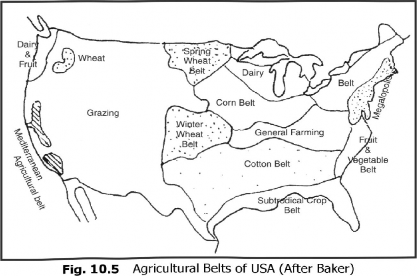
(ii) Single-Element Technique: This is an arbitrary technique in which only the first ranking crops in respect of area are plotted for the purpose of demarcation of agricultural regions. Baker was the first geographer who adopted the single-element technique for the demarcation of agricultural belts of U.S.A. This technique has however been criticized as it is not scientific and objective (Fig. 10.5). On the basis of this technique, the first ranking crops of India in the different districts in 2005-06 have been plotted in Fig. 10.1 which show the rice, wheat, maize, bajara, ragi, millets, cotton, and groundnut regions.
The main weakness of this technique is that it conceals the position and importance of other crops grown in the region. In fact, in most of the districts of India, crops are grown in combination and not in isolation. A combinational analysis is more important from the agricultural planning point of view than that of the single dominant crop.
(iii) Multi-Element or Statistical Technique: The multi element technique is more objective and scientific. In the statistical techniques more than one elements (crops, etc.) are taken into consideration. The crop combination regions demarcated by Weaver, Doi, Coppock, Shafi, Tashir Singh, Aiyer, Husain, Sapre, and Deshpande, Tiwari etc., were based on the Standard Deviation Technique. This technique is free from bias and subjectivity.
Class VII: Fairly well suited for grazing or forestry with little carrying capacity of livestock.
Class VIII: Suited only for wildlife. This land has severe climate, wet soil, stones, bad lands, sandy beaches, marshes, deserts, and nearly barren lands.
