RIVER BASINS OF INDIA
Rivers with their tributaries are the main channels of drainage of the land surface; they are at the same time also the chief agents of land-erosion, and the main lines for transport waste-products of the land to the sea. The area drained by the main river including all its tributaries is known as its drainage basin. On the basis of the area drained, the river basins of India have been classified into three categories: (i) river basins with catchment area of more than 20,000 sq km known as large river basins; (ii) river basins having a catchment area between 2000 to 20,000 sq km known as the medium basins, and (iii) the rivers having a catchment area less than 2000 sq km known as minor river basins. India has one hundred and thirteen river basins, of which 14 are large, 44 medium and 55 minor river basins. The major river basins of India in descending order of area are; the Ganga, Indus, Godavari, Krishna, Brahmaputra, Luni, Mahanadi, Narmada, Kaveri, Tapi, Pennar, Brahmani, Mairi, Sabannati, Barak, and Subarnarekha. The major river basins form about 84 per cent of the total drainage area of the country (Fig. 3.4).
The three major river systems (Ganga, Indus, and Brahmaputra) are international rivers. The Indus and some of its important tributaries traverse Tibet (China), India, and Pakistan, while the
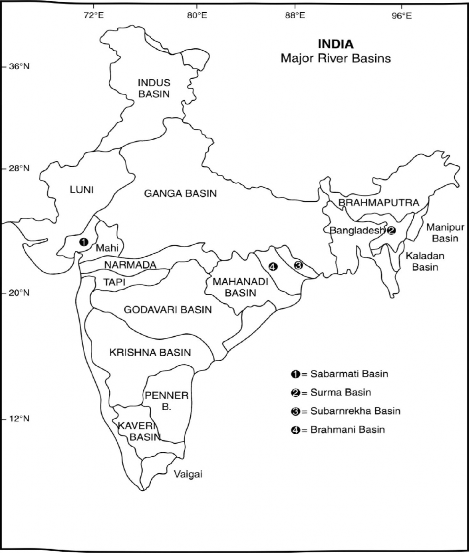
Fig. 3.4 Major River Basins
Ganga and Brahmaputra, and their tributaries cross Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh. The main river basins, their basin area, and annual discharge has been shown in Table 3.1.
On the basis of mode of origin, the drainage oflndia may be divided into (i) Himalayan or the Extra-Peninsular Drainage, and (ii) the Peninsular Drainage.
There is no clearcut line of demarcation between these two drainage systems, as many of the Peninsular rivers like the Chambal, Betwa, Sind, Ken, and Son are much older in age and origin than the Himalayan rivers.
Table 3.1 Major Rivers oflndia and their Surface Flow
River Basin | Basin Area * | Percentage area | Annual Discharge (M‘/km2) | % |
Ganga | 861,4-04 | 26.2 | 468,700 | 25.2 |
Indus | 321,284 | 9.8 | 79,500 | 4.3 |
Godavari | 312,812 | 9.5 | 118,000 | 6.4 |
Krishna | 258,948 | 7.9 | 62,800 | 3.4 |
Brahmaputra | 258,008 | 7.8 | 627,000 | 33.8 |
Mahanadi | 141,589 | 4.3 | 66,640 | 3.6 |
Narmada | 98,795 | 3.0 | 54,600 | 2.9 |
Kaveri | 87,900 | 2.7 | 20,950 | 1.1 |
Tapi | 65,150 | 2.0 | 17,982 | 0.9 |





Pennar | 55,213 | 1.7 | 3,238 | 0.2 |
Brahmani | 39,033 | 1.2 | 18310 | 1.0 |
Mahi | 34,481 | 1.0 | 11,800 | 0.6 |
Subarnarekha | 19,296 | 0.6 | 7,940 | 0.4 |
Sabarmati | 21,895 | 0.7 | 3,800 | 0.2 |
Medium and Minor Rivers | 711,833 | 23.6 | — | 16.0 |
Total (India) | 3 2 8,76,97 | 100.00 | 1,561,170 | 100.00 |
’•'Area means basin area in India. Source: S.P. Das Gupta, 1989.
