Soil Components
Clay: very find particles. Compacts easily. Forms large, dense clumps when wet. Low permeability to water; therefore, upper layers become waterlogged.
Gravel: Coarse particles. Consists of rock fragments.
Loam: About equal mixtures of clay, sand, slit, and humus. Rich in nutrients. Holds water but does not become waterlogged.
Sand: Sedimentary material coarser than slit. Water flows through too quickly for most crops. Good for crops and plants requiring low amounts of water.
Slit: Sedimentary material consisting of very fine particles between the size of sand and clay. Easily transported by water.
♤ Soil is a natural body of mineral and organic constituents differentiated into horizons usually unconsolidated, of variable depth which differs among themselves as well as from the underlying parent material in morphology, physical makeup, chemical properties and composition and biological characteristics.
♤ Soil profile: The vertical section of the soil showing the various layers from the surface to the unaffected parent material is known as a soil profile. The various layers are known as horizons.
♤ There are 5 master horizons in the soil profile. Not all soil profiles contain all 5 horizons; and so, soil profiles differ from one location to another.
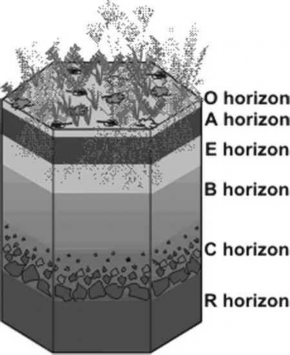
Soil Profile
♤ The 5 master horizons are represented by the letters: O, A, E, B, and C.
♤ O: The O horizon is a surface horizon that is comprised of organic material at various stages of decomposition. It is most prominent in forested areas where there is the accumulation of debris fallen from trees.
♤ A: The A horizon is a surface horizon that largely consists of minerals (sand, silt, and clay) and with appreciable amounts of organic matter. This horizon is predominantly the surface layer of many soils in grasslands and agricultural lands.
♤ E: The E horizon is a subsurface horizon that has been heavily leached. Leaching is the process in which soluble nutrients are lost from the soil due to precipitation or irrigation. The horizon is typically light in color. It is generally found beneath the O horizon.
♤ B: The B horizon is a subsurface horizon that has accumulated from the layer(s) above. It is a site of deposition of certain minerals that have leached from the layer(s) above.
♤ C: The C horizon is a subsurface horizon. It is the least weathered horizon. Also known as the saprolite, it is unconsolidated, loose parent material.
♤ R: Unweathered rock exists below the parent material.
♤ Soil texture refers to the relative proportion of particles or it is the relative percentage by weight of the three soil separates viz., sand, silt and clay or simply refers to the size of soil particles.
♤ Loam: A type of soil texture with good water holding capacity and drainage suitable for cultivation of variety of crops.
♤ Soil structure: The arrangement and organization of primary and secondary particles in a soil mass is
known as soil structure.
Saline soils
♤ Saline soils are characterised by higher amount of water soluble salt, due to which the crop growth is affected.
Sodic soils
♤ Sodic soils are characterised by the predominance of sodium in the complex with the exchangeable sodium percentage exceeding 15 per cent and the pH more than 8.5.
Acid soils
♤ Acid soils are characteristically low in pH ( < 6.0). Predominance of H + and Al3+ cause acidity resulting in deficiency of P, K, Ca, Mg, Mo and B.
Sandy soils
♤ Sandy soils are containing predominant amounts of sand resulting in higher percolation rates and nutrient losses.
♤ Alkaline soil: A soil with pH above 7, usually above 8.5 are considered alkaline. Alkaline soils often occur in arid regions that receive less than 25 inches of rain per year.
♤ Calcariuos soil- Soils with kankar nodules in the plough zone and subsoil.
♤ Alfisol: Soils with grey to brown surface horizons, medium to high supply of bases and B horizons of illuvial clay accumulation. These soils formed mostly under forest or savanna vegetation in climates with slight to pronounced seasonal moisture deficit.
♤ Aridisol: Minerals soils that have an aridic moisture regime. These are desert soil.
