19.1.1. Change in equilibrium
♤ The equilibrium between the formation and destruction of ozone, has been upset by the influx of several substances into the atmosphere which react with ozone and destroy it.
♤ The rate at which ozone is being destroyed is much faster than the rate at which it is being formed.
♤ It implies that there is a significant decrease in the concentration of ozone in a particular region of the atmosphere, hence the name ‘Ozone Depletion’.
♤ The best example of such an Ozone Depletion is the atmosphere over the Antarctic which has only about 50 percent of the ozone that originally occurred there. The actual realization of ozone-depletion came only in 1985.
19.1.2. Sources
chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs):
CFCs molecules are made up of chlorine, fluorine and carbon.
Where it is used?
They are used as refrigerants, propellents in aerosol sprays, foaming agents in plastic manufacturing, fire extinguishing agents, solvents for cleaning electronic and metallic components, for freezing foods etc .
Two-thirds of CFC is used as refrigerants while one-third is used as blowing agents in foam insulation products.
Why CFCs are used?
CFCs has a wide and varied application due to its properties like non-corrosiveness, non-inflammability, low toxicity and chemical stability, etc.
Lifetime & removal of CFCs
Unlike other chemicals, CFCs cannot be eliminated from the atmosphere by the usual scavenging processes like photodissociation, rain-out and oxidation.
In fact, the residence time of CFCs in the atmosphere estimated to be between 40 and 150 years. During this period, the CFCs move upwards by random diffusion, from the troposphere to the stratosphere.
The escape of CFCs
The CFCs enter into the atmosphere by gradual evaporation from their source. CFCs can escape into the atmosphere from a discarded refrigerator. Since the CFCs are thermally stable they can survive in the troposphere. But in the stratosphere, they are exposed to UV radiation.
The chemical reaction
The molecules of CFCs when exposed to UV radiation break up, thus freeing chlorine atoms. A free chlorine atom reacts with an ozone molecule to form chlorine monoxide (ClO). The molecules of chlorine monoxide further combine with an atom of oxygen. This reaction results in the formation of an oxygen molecule (O2) and reformation of the free chlorine atom (CI).
Chlorine +---> Chlorine monoxide--->
+ monoxide (o) Net reaction:
Chlorine monoxide + oxygen
Chlorine + Oxygen

ozone +---► oxygen + oxygen

monoxide (o)

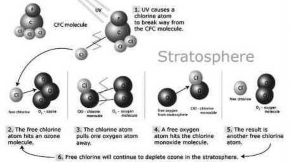
CFC Ozone Depletion
The depletion of O3 is catalystic. The element that destroys O3 (i.e chlorine) is being reformed at the end of cycle. A single chlorine atom destroys thousands of ozone molecules before encountering reactive nitrogen or hydrogen compounds that eventually return chlorine to its reservoirs.
Do you know?
Barking deer /common muntjac is the mammal with the lowest recorded chromosome number. It gives calls similar to barking, usually on sensing a predator. Status - least threatened.
