17.2. GREENHOUSE EFFECT
The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon that blankets the earth lower atmosphere and warms it, maintaining the temperature suitable for living things to survive.
Just as greenhouses, that keeps the air warm inside its chamber, water vapor and green house gases warms the Earth. Greenhouse gases play an important role in the balance of Earth’s cooling and warming.
According to one estimate, in the absence of naturally occurring green house effect, the average temperature of the earth surface would be -19°C instead of present value of 15°C and the earth would be a frozen lifeless planet.

Green House
17.2.1. What is the Greenhouse Effect?

The greenhouse effect is a process (similar to green house) caused by greenhouse gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere. This process plays a crucial role in warming the Earth’s surface, making it habitable.
However, human-generated greenhouse gas emissions upset the natural balance and lead to increased warmth.
A greenhouse/ glasshouse is a building made of glass chambers in which plants are grown in cold countries or in cold climate areas. There is a continued increase in temperature in green house even when the outside temperature remained low. It protects plants from frost.
Do you know?

Tree rings provide precise information about environmental events, including volcanic eruptions.
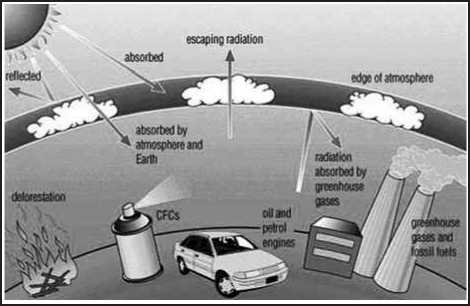

Incoming Energy
♤ The Sun emits energy that is transmitted to Earth. Because the Sun is very hot, the energy is emitted in high-energy short wavelengths that penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere.
Absorption
♤ About 30% of the Sun’s energy is reflected directly back into space by the atmosphere, clouds, and surface of the Earth. The rest of the Sun’s energy is absorbed into the Earth’s system.
Emission
♤ The Earth re-emits energy back into the atmosphere. Because the Earth is cooler than the Sun, the energy is emitted in the form of infrared radiation, at wavelengths longer than the incoming solar energy.
Role of Greenhouse Gases
♤ Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb much of the long-wave energy (infrared radiation) emitted from the Earth’s surface, preventing it from escaping from the Earth’s system. The greenhouse gases then re-emit this energy in all directions, warming the Earth’s surface and lower atmosphere.
Human Role
♤ The atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly over the past two centuries, largely due to human-generated carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels, deforestation.
♤ This increase has amplified the natural greenhouse effect by trapping more of the energy emitted by the Earth. This change causes Earth’s surface temperature to increase.
Do you know?
♤ No tree dies of old age. They are generally killed by insects, disease or by people.
♤ Trees grow from the top, not from the bottom as is commonly believed.
♤ Tree leaves help trap and remove tiny particles of soot and dust which otherwise damages human lungs.
♤ Tree root networks filter contaminants in soils producing clean water.
♤ Trees prevent erosion by trapping soil that would otherwise become silt
