*NIC – National Industries Classification
2. Evolution of the Food Processing Sector in India
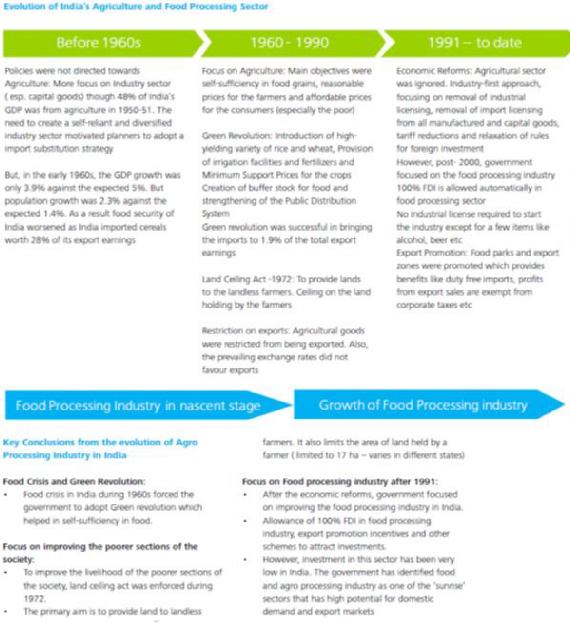
3. Supply Chain of the Food Processing Sector
A supply chain is a network between suppliers (farmers) of raw material, company (food processor) and distribution network to market the finished products. Supply chain represents the steps it takes to get the product or service to the customer.
The different stages of processing of manufactured food products are as follows:
Source: Data Bank on Economic Parameters of the Food Processing Sector
♤ Primary Processing: cleaning, grading, powdering and refining of agricultural produce, e.g., grinding wheat into flour.
♤ Secondary Processing: basic value addition, e.g., tomato-puree, ground coffee, processing of meat products.
♤ Tertiary Processing: high value addition products like jams, sauces, biscuits and other bakery products ready for consumption
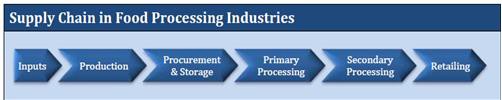
The generic value chain of the food processing industry from raw materials to retail to the consumer is shown below in the figure.
3.1. Backward and Forward Linkages
Backward Linkage: It means the connectivity of the FPIs with sources of raw material supply. For example, supply of raw material like tomatoes to a ketchup manufacturer.
Forward Linkage: It means the connectivity of FPIs with the markets through distribution network comprising of physical infra like storages, road and rail network etc.
