The major and medium irrigation projects are further classified as:
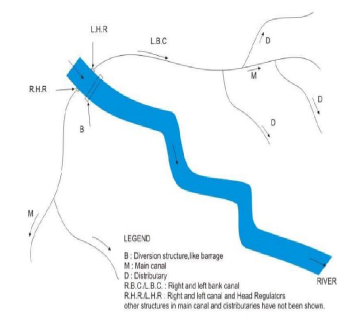
An Example of Direct Irrigation
1. Direct Irrigation method: In this project water is directly diverted from the river into the canal by constructing a diversion structure like weir or barrage across the river with some pondage to take care of diurnal variations. It also effects in raising the river water level which is then able to flow into the offtaking channel by gravity. The flow in the channel is usually controlled by a gated structure and this in combination with the diversion structure is also sometimes called the headworks.
A direct irrigation scheme of irrigation using
river water diversion head works typically be laid out as shown in the adjoining figure.
An example of this scheme is the DVC irrigation project on the Damodar river with the barrage located at Durgapur.
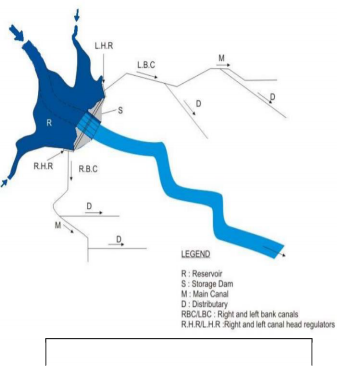
2. Storage Irrigation Method: For this type of irrigation schemes part of the excess water of a river during monsoon which otherwise would have passed down the river as a flood is stored in a reservoir or tank found at the upstream of a dam constructed across a river or stream. This stored water is
then used for irrigation. This is adopted when the flow of river or stream is in excess of the requirements of irrigated crops during a certain part of the year but falls below requirements or is not available at all in the river during remaining part of the year. Since the construction site of a storage reservoir is possible in regions of undulating topography, it is usually practiced in non-deltaic areas. A general layout of this irrigation scheme may typically be laid out as shown in the adjoining Figure.
An Example of Storage Irrigation Scheme
In other type of scheme the storage head works or the dams has to be equipped with ancillary structure like outlet, sluice, spillway, log chutes, etc. The storage created by the dam behind the reservoir is substantial compared to that behind a barrage and may inundate a large tract of land, depending on the topography. The capacity of the reservoir is generally determined systematically by knowing possible withdrawal demands (in this case for irrigation) over the weeks and months of a year and corresponding expected inflows. An example for this type of scheme is the Indira Sagar project on the Narmada River.
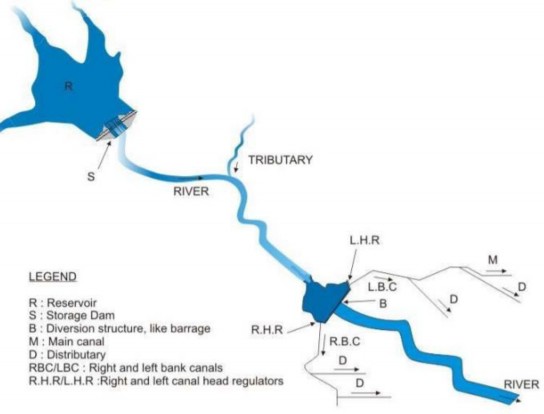
Figure: A Typical Layout of Storage irrigation scheme incorporating a dam with a barrage on its downstream
Another type of storage irrigation method envisages the storage of water at some place in the hilly terrain of the river where the construction of the dam is possible. A barrage is constructed at some downstream location, where the terrain is flatter and canals take off as in a usual direct irrigation method. A general layout of such scheme could be represented as shown in Figure below.
An example for this type of scheme is the Bhakra-dam Nangal-barrage combination on the river Sutlej.
