5. Observing Migration Trends in Census
A few facts pertaining to the internal migration (within the country) and international migration (out of the country and into the country from other countries) are presented in this section. Under the internal migration, four streams are identified:
♤ Rural to rural (R-R);
♤ Rural to urban (R-U);
♤ Urban to urban (U-U); and
♤ Urban to rural (U-R).
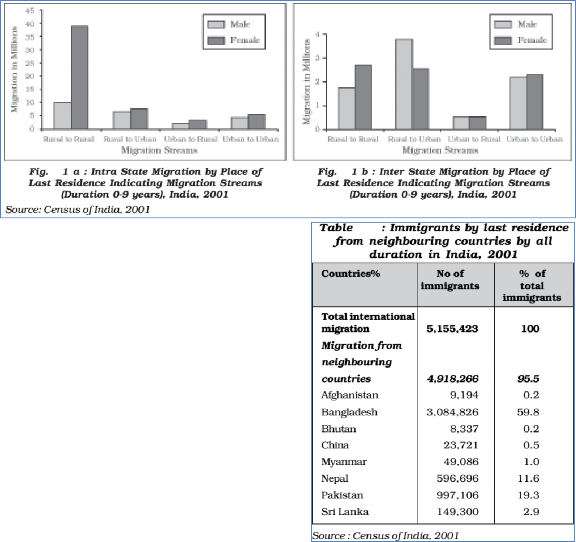
In India, during 2001, out of 315 million migrants, enumerated on the basis of the last residence, 98 million had changed their place of residence in the last ten years. Out of these, 81 million were intra-state migrants. The stream was dominated by female migrants. Most of these were migrants related to marriage. The distribution of male and female migrants in different streams of intra-state and inter-state migration is presented in Fig. 1a and 1b below. It is clearly evident that females predominate the streams of short distance rural to rural migration in both types of migration. Contrary to this, men dominate the rural to urban stream of inter-state migration due to economic reasons.
Apart from these streams of internal migration, India also experiences immigration from and emigration to the neighbouring countries. The table (in right) presents the details of migrants from neighbouring countries. Indian Census 2001 has recorded that more than 5 million person have migrated to India from other countries. Out of these, 96 per cent came from the neighbouring countries: Bangladesh (3.0 million) followed by Pakistan (0.9 million) and Nepal (0.5 million). Included in this are 0.16 million refugees from Tibet, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, and Myanmar. As far as emigration from India is concerned it is estimated that there are around 20 million people of Indian Diaspora, spread across 110 countries.
