3. What are the Different Forms of Migration?
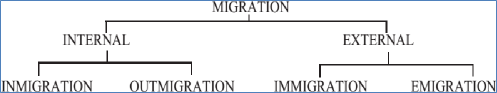
People may move within a country between different states or between different districts of the same state or they may move between different countries. Therefore, different terms are used for internal and external migration. Internal migration refers to migration from one place to another within a country, while external migration or international migration refers to migration from one country to another.
a) Immigration and Emigration: ‘Immigration’ refers to migration into a country from another country and ‘emigration’ refers to migration out of the country. These terms are used only in connection with international migration. For example migrants leaving India to settle down in the United States or Canada are immigrants to the United States or Canada and emigrants from India.
b) In Migration and Outmigration: These are used only in connection with internal migration. ‘In migration’ refers to migration into a particular area while ‘out migration’ refers to movements out of a particular area. Thus, migrants who come from Bihar or Uttar Pradesh to Punjab are considered to be immigrants for Punjab and out migrants for Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
The term ‘in migration’ is used with reference to the area of destination of the migrants and the term ‘outmigration’ is used with reference to the area of origin or place of departure of the migrant.
The main forms of migration can be summarized in a chart.
Typology based on time classified migration into long range migration and short range or seasonal migration. When a move is made for a longer period, it is called long range migration. However, when there is permanent shift of population from one region to another, it is known as permanent migration. But when people shift to the sites of temporary work and residence for some or several months, it is known as periodic or seasonal migration. For example, during peak agricultural season excess labour is required, and people from the neighbouring areas come in. The custom of women returning to her parents to deliver her first child also accounts for significant short range internal migration.
Apart from these two important types, migration could be voluntary or involuntary or forced brain drain (migration of young skilled persons) and migration of refugees and displaced persons.
