2.1.1. Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
Regional rural banks came into being in the 1970s with the objective of providing deposit and credit facilities to the people in rural areas especially weaker sections like the small and marginal farmers, agricultural laborers, small entrepreneurs etc. Therefore, they are also usually knows as ‘Small Man’s Bank.’ Even though these banks count as the scheduled commercial banks but their focus and reach is generally limited to a district or two. Some of the examples of Regional Rural Banks are Assam Gramin Vikash Bank, Allahabad UP Gramin Bank, Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank etc.
♤ These banks are set up by the public sector banks and the PSB which set up a particular RRB is called sponsor bank of that RRB. It is required to subscribe to the share capital of RRBs, train their personnel and provide managerial and financial assistance.
♤ RRBs were set with following aims:
o To increase the credit flow to rural areas
o To lend to weaker sections at concessional rates
From 1997, RRBs were freed to lend outside the target group. Now merging of RRBs is going on as many of the RRBs became unviable or less profitable. Therefore, weak banks are being merged with efficient banks. Now, they gain more autonomous powers also.
The priority sector lending target for RRBs is 75% of the total outstanding loans.
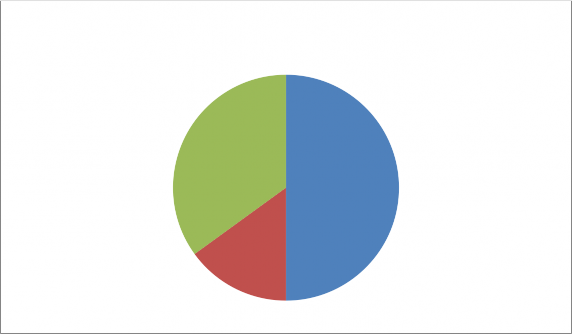
Contribution in RRBs
Sponsor bank
35%
Government of
India 50%
State
government 15%
The Government of India, the concerned State Government and the bank, which had sponsored the RRB contribution to the share capital of RRBs is shown in the chart below:
