1. Dams
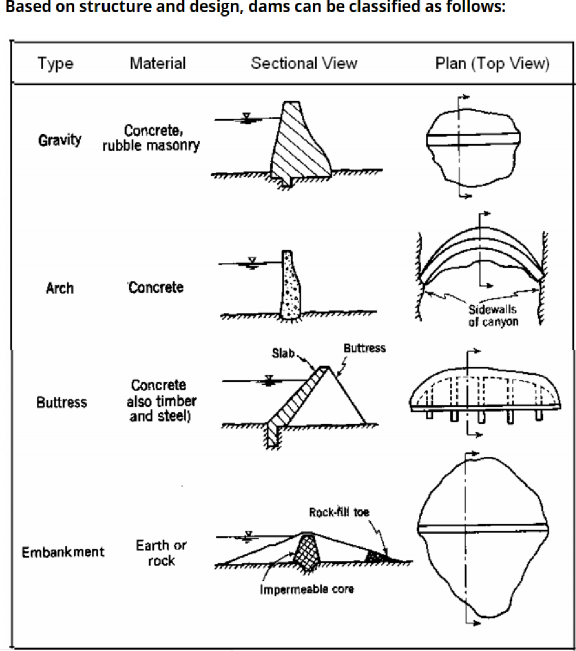
A dam is a hydraulic structure constructed across a river to store water on its upstream side. It is an impervious or fairly impervious barrier put across a natural stream so that a reservoir is formed. On the basis of structure, dams can be categorized as:-
A. Gravity Dams: These dams are heavy and massive wall-like structures of concrete in which the whole weight acts vertically downwards. These dams resist the horizontal thrust of the water entirely by their own weight.
B. Buttress Dam: is a gravity dam reinforced by structural supports. These dams have a solid, water-tight upstream side that is supported at intervals on the downstream side by a series of buttresses or supports.
C. Earth Dams: They are trapezoidal in shape. Earth dams are constructed where the foundation or the underlying material or rocks are weak to support the masonry dam or where the suitable competent rocks are at greater depth.
D. Arch Dams: These are designed so that the force of the water against it, known as hydrostatic pressure, presses against the arch, compressing and strengthening the structure as it pushes into its foundation or abutments.